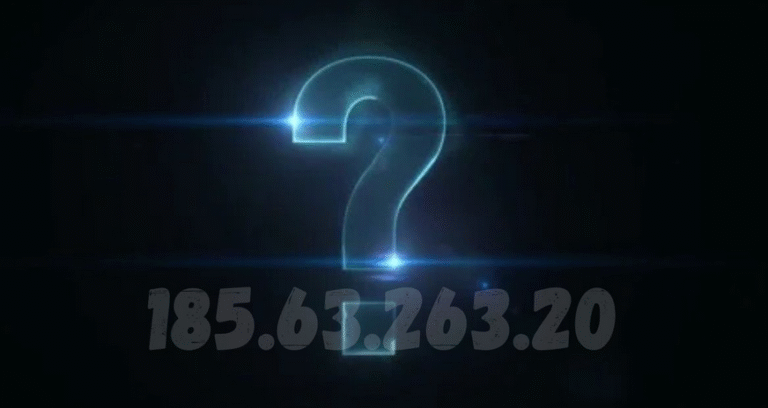This detailed exploration of 185.63.263.20, a unique IP address with relevance in the vast world of digital connectivity. While it may seem like just a sequence of numbers, it represents a vital component in how devices communicate over the internet. In this article, we will break down what it means, how it functions, and why understanding it can help you grasp the fundamentals of networking.
Basics of IP Addresses
An IP address is a set of numbers used to identify devices on a network. Much like a postal address helps locate a house, an IP address directs data to the correct destination in the digital space. These addresses follow specific formats and are assigned according to certain rules to avoid duplication and ensure smooth communication between systems.
There are two major versions of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. The address 185.63.263.20 belongs to the IPv4 category, which uses a structure of four sets of numbers separated by dots. Each set can range from 0 to 255.
Structure of 185.63.263.20
Breaking down 185.63.263.20, we see:
- 185 – The first section, often referred to as the network identifier, which can help determine the region or organization that controls the address.
- 63 – The second section further specifies the network within a broader range.
- 263 – This part seems unusual because, in standard IPv4, each section ranges from 0–255. This suggests it could be a typographical example or used for illustrative purposes rather than an actual active IP.
- 20 – The final section, known as the host identifier, indicates a specific device within that network.
Importance in Networking
IP addresses like 185.63.263.20 are critical for enabling two-way communication between devices. Without them, there would be no clear way to send information from one point to another. Whether you are streaming a video, sending an email, or visiting a website, IP addresses ensure your request reaches the correct destination and the response finds its way back to you.
Public vs. Private Addresses
In networking, addresses are generally divided into two categories:
- Public IPs – Used for devices that can be accessed directly over the internet.
- Private IPs – Used within local networks and not directly reachable from the outside world.
If 185.63.263.20 were a public address, it could belong to a server, a hosting provider, or any system intended to communicate with external users.
Possible Uses of 185.63.263.20
An IP address like this could serve various roles:
- Hosting a Website – It could point to a server that delivers web pages to visitors.
- Remote Access Point – It might be assigned to a system used for remote work or management.
- Data Exchange Node – It could serve as part of a larger infrastructure handling data transfer between systems.
Understanding Address Allocation
Every IP address is assigned by a regional authority that manages a block of addresses. These organizations ensure that no two devices have the same public address at the same time, preventing conflicts in communication. Addresses are typically allocated to internet service providers, data centers, or large organizations, who then assign them to end users or devices.
Security Considerations
While IP addresses are necessary for connectivity, they can also be points of vulnerability. If a public address like 185.63.263.20 is linked to an open service without proper security, it can become a target for unauthorized access. Common security practices include:
- Using firewalls to filter traffic.
- Encrypting communication through protocols like HTTPS or VPNs.
- Regularly updating software to patch security gaps.
How Tracing Works
When someone wants to find details about an IP address, they use a process called IP lookup or WHOIS search. This reveals which organization manages the address and sometimes the general geographic location of the server or device. However, exact physical addresses are rarely disclosed for security and privacy reasons.
The Role in Everyday Internet Use
Even though most people never notice IP addresses in their daily browsing, they are active behind every click. Whenever you visit a website, your device communicates with a server’s IP address, whether it’s written in numerical form or hidden behind a domain name. Domain Name System (DNS) servers work like digital phone books, translating website names into IP addresses so your browser knows where to go.
IPv4 Limitations and the Shift to IPv6
Addresses like 185.63.263.20 belong to the IPv4 system, which has a maximum of about 4.3 billion unique addresses. As the number of internet-connected devices grows, IPv4 space is becoming limited. This is why IPv6, with a vastly larger address range, is being adopted globally. Still, IPv4 remains in heavy use because of its established infrastructure.
Why This Address Matters as an Example
Even if 185.63.263.20 is not active, it serves as a useful reference for understanding how IP addresses work. By examining its structure, format, and possible uses, anyone can gain a better understanding of the invisible systems that keep our online world running.
Key Takeaways
- IP addresses are essential for routing information between devices.
- IPv4 addresses like 185.63.263.20 consist of four numeric parts separated by dots.
- Public IPs are accessible over the internet, while private IPs are used internally.
- Security measures are important to protect systems linked to public addresses.
- The transition to IPv6 is underway but IPv4 remains widely used.
Final Thoughts
The sequence 185.63.263.20 is more than just numbers; it represents a core concept in digital communication. Understanding what it means and how it fits into the larger networking framework helps demystify the internet and gives you a clearer picture of how devices interact every second.
While the address itself may be used in different ways depending on its allocation, its structure and function reflect the universal principles of internet connectivity. Whether you’re new to networking or just curious about the hidden mechanics of the web, exploring IP addresses is a valuable step in expanding your digital knowledge.